MTHFR Gene: Top 10 Things That You Need To Know

Table of Contents
What is the MTHFR Gene?
The Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene is responsible for producing an enzyme that plays a critical role in processing amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. Specifically, this enzyme converts a molecule called 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, a precursor of a type of B vitamin called folate.
MTHFR Gene: The Basics
The Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene is a part of the human DNA, located on chromosome 1. This gene contains the information required to produce the MTHFR enzyme, a key player in the metabolism of folate, a type of B vitamin.
Role of MTHFR in Folate Metabolism
Folate plays a critical role in the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and proteins. The MTHFR enzyme specifically converts a molecule known as 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate into 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, a reaction vital to the folate metabolic process. This conversion facilitates the remethylation of homocysteine to methionine, an essential amino acid, keeping homocysteine levels within a normal range.
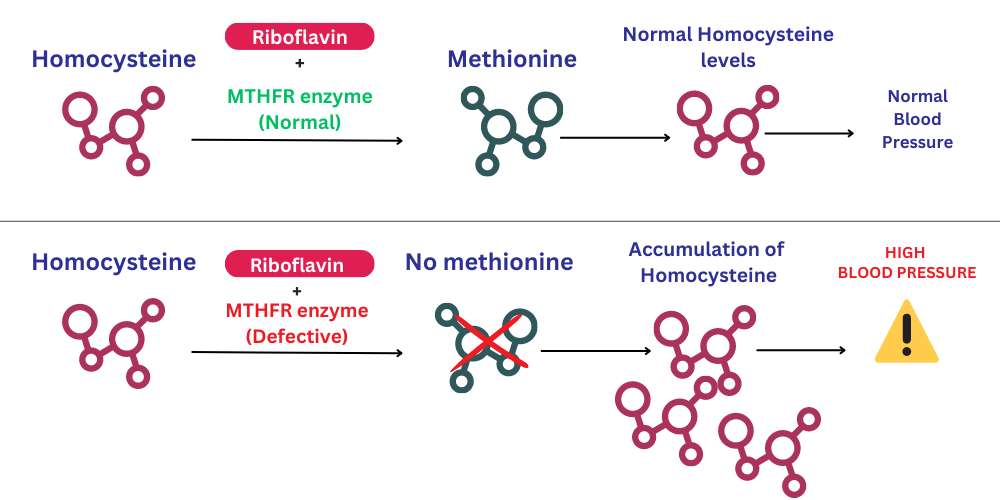
MTHFR’s Impact on Cellular Function
Methionine, a product of the MTHFR enzyme’s activity, is further processed to create S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), a universal methyl donor for over 100 different substrates, including DNA, RNA, proteins, and lipids. This process is crucial in controlling gene expression and maintaining cellular function.
Importance of MTHFR in Human Health
Given its role in folate metabolism and methylation process, the MTHFR gene is crucial for human health. It affects various biological processes, including DNA synthesis and repair, cell division, and amino acid metabolism. Additionally, because of its role in regulating homocysteine levels, this gene is significant for cardiovascular health.
MTHFR Variations and Health Implications
Certain variants or mutations in the MTHFR gene can affect its function, leading to reduced enzyme activity. This could result in high levels of homocysteine in the blood, a risk factor for several health conditions including heart disease, stroke, and certain mental disorders. However, the presence of these mutations doesn’t guarantee the development of these conditions; other genetic and environmental factors also come into play
What is an MTHFR Gene Mutation?
Understanding Gene Mutations
Before delving into MTHFR gene mutations, it’s essential to understand what a gene mutation is. A mutation is a change that occurs in our DNA sequence, either due to errors when the DNA duplicates or as a result of environmental factors such as UV light and cigarette smoke.
MTHFR Gene Mutation: An Overview
An MTHFR gene mutation is a change in the MTHFR gene that can impact the MTHFR enzyme’s function. These mutations can decrease the enzyme’s ability to process folate and homocysteine, potentially leading to health issues.
Common MTHFR Mutations: C677T and A1298C
Two common mutations occur in the MTHFR gene: C677T and A1298C. Both mutations can reduce the activity of the MTHFR enzyme, but C677T is generally associated with a more significant reduction. People can inherit one or both of these mutations from their parents, which can compound the enzyme’s deficiency.
| SNP ID | Gene | Mutation | Position | Major Allele | Minor Allele | Risk Allele | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1801133 | MTHFR | C677T | 11q23.3 | C (cytosine) | T (thymine) | T | Moderate |
| rs1801131 | MTHFR | A1298C | 11q23.3 | A (adenine) | C (cytosine) | C | Low |
Note
- The SNP ID corresponds to the identification tag used by databases to track individual SNPs.
- The “Gene” column refers to the gene where the SNP is located.
- “Mutation” signifies the type of mutation represented by the SNP.
- “Position” indicates the exact location of the gene on the chromosome.
- The “Major Allele” is the most common version of the SNP in the general population, and the “Minor Allele” is the less common version.
- The “Risk Allele” refers to the allele associated with increased risk for the condition in question.
- The “Impact” column provides a general idea of the impact of the SNP. This could be “High”, “Moderate”, or “Low”, depending on the severity of the associated risk.
Impact of MTHFR Gene Mutations on Health
MTHFR mutations can contribute to elevated levels of homocysteine in the blood, known as hyperhomocysteinemia. This condition is a potential risk factor for cardiovascular disease and other health issues. Some studies also link MTHFR mutations to a higher risk of certain cancers, neural tube defects, psychiatric disorders, and pregnancy complications, although more research is needed in these areas.
It’s Not Just About the Genes
It’s essential to note that having an MTHFR mutation doesn’t guarantee health issues. Many factors, including overall health, lifestyle, and dietary choices, can influence how this mutation affects an individual. Furthermore, certain nutritional supplements, such as folic acid or methylated folate, may help manage health risks associated with MTHFR mutations. As always, individuals should consult with a healthcare provider or a genetic counselor to understand what an MTHFR mutation means for them.
What is MTHFR C677T Gene Mutation?
MTHFR C677T is one of the most commonly studied mutations in the MTHFR gene. Individuals who inherit two copies of C677T (one from each parent) have an increased risk of developing certain health conditions, such as heart disease, stroke, and neural tube defects.
Check out our MTHFR sample report video
Is the MTHFR Gene Mutation Clinically Significant?
While the MTHFR gene mutations have been associated with an increased risk of certain health conditions, the clinical significance of these mutations is controversial. Many people with MTHFR gene mutations do not experience any health problems. Moreover, it’s important to note that other genetic and environmental factors also influence the risk of developing these conditions.
What are the Symptoms of MTHFR Gene Mutation?
While the symptoms associated with MTHFR gene mutations can be diverse and vary significantly among individuals, some of the commonly reported symptoms are:
- Cardiovascular and Thromboembolic Disorders: These may manifest as recurrent venous thrombosis, stroke, or heart attack.
- Mental Disorders: Mental health issues, such as depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia, have been reported in some individuals with MTHFR gene mutations.
- Pregnancy Complications: Some studies suggest a link between MTHFR gene mutations and complications during pregnancy, such as preeclampsia, recurrent miscarriages, and neural tube defects in babies.
- Bone Health Issues: MTHFR mutations have been associated with an increased risk of osteoporosis and other bone health problems.
- Elevated Homocysteine Levels: Homocysteine is a type of amino acid produced by your body, usually in response to the consumption of meat. Elevated homocysteine levels are commonly found in people with MTHFR mutations.
- Autoimmune Disorders: These may include conditions like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and autoimmune thyroid disorders.
- Chronic Pain and Fatigue: Some people with MTHFR mutations may experience fibromyalgia or chronic fatigue syndrome.
It’s essential to note that the presence of these symptoms doesn’t necessarily mean that an individual has an MTHFR mutation. Similarly, having an MTHFR mutation does not guarantee that these symptoms will occur. Many factors, including lifestyle, environmental factors, and other genetic factors, contribute to the expression of these symptoms. Always consult with a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Does the MTHFR Gene Cause Autism?
Although some studies have suggested a potential link between MTHFR gene mutations and autism, these findings have been inconsistent, and more research is needed to confirm this relationship.
Can MTHFR Gene Cause Miscarriage?
Several studies have suggested a possible association between MTHFR gene mutations and an increased risk of miscarriage. However, the evidence is not strong enough to establish a direct causal relationship, and further research is needed.
How to Know if You Have an MTHFR Gene Mutation
The presence of an MTHFR gene mutation can be determined through genetic testing, which usually involves a blood test.
How to Test for MTHFR Gene Mutation
Testing for MTHFR gene mutations typically involves a blood test. This can be done as part of a general genetic screening or when a specific condition associated with the mutations is suspected [1].
What Causes MTHFR Gene Mutation?
MTHFR gene mutations are inherited, meaning they are passed down from parents to their children. Each person has two copies of the MTHFR gene, one inherited from each parent. If one or both parents have a mutation in one or both of their MTHFR genes, they may pass this mutation on to their child.
Does 23andMe Test for MTHFR Gene?
The 23andMe health and ancestry service does not provide data on the MTHFR gene due to the lack of consensus within the medical community about whether testing for these variants is clinically useful [5].
FAQs
-
What are the possible health implications of MTHFR gene mutations?
MTHFR gene mutations have been associated with an increased risk of several health conditions, including heart disease, stroke, and neural tube defects. However, many people with these mutations do not develop these conditions.
-
Are there treatments for conditions caused by MTHFR gene mutations?
While there are no treatments specifically for MTHFR gene mutations, conditions associated with these mutations, such as high homocysteine levels, can often be managed with lifestyle changes and medications.
References
- National Library of Medicine. MTHFR gene. Genetics Home Reference.
- Schwahn B, Rozen R. Polymorphisms in the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene: clinical consequences. Am J Pharmacogenomics. 2001;1(3):189-201.
- Mohammad NS, et al. Aberrations in folate metabolic pathway and altered susceptibility to autism. Psychiatr Genet. 2009;19(4):171-176.
- George L, Mills JL, Johansson ALV, et al. Plasma folate levels and risk of spontaneous abortion. JAMA. 2002;288(15):1867-1873.
- 23andMe Customer Care
Written By
Share this article











